


Top 10
Mosasaurs
At the beginning of the Late Cretaceous the mosasaurs were small unassuming predators that frequented coastal areas. By the end of the Cretaceous they were the apex predators of the oceans. Few other animal groups can claim to be so successful, so let’s take a look at ten of the most significant mosasaurs.
10 - Halisaurus
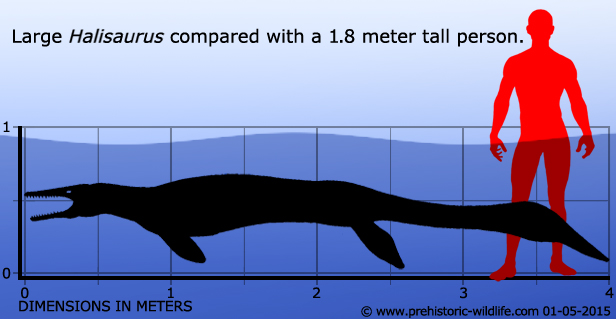
Halisaurus was on the smaller end of the scale for mosasaur size, but is a good example of how some mosasaurs evolved to be fast and agile hunters of fish. Mosasaurs such as Halisaurus evolved to fill a gap that had been largely left void by the ichthyosaurs when they disappeared from the world’s oceans earlier in the Cretaceous. Halisaurus was so successful in this that individuals have been recovered from North America, South America, Europe and Africa.
9 - Plotosaurus
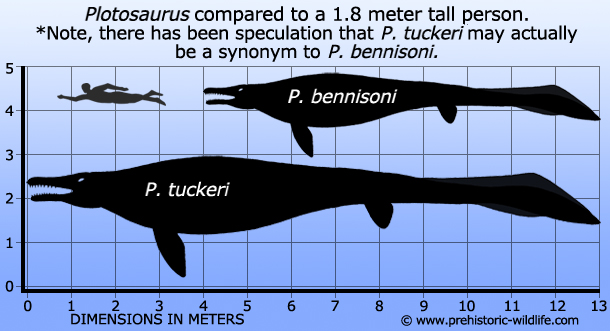
Plotosaurus is one of the larger mosasaurs and one that may have a specialised ecological niche. Plotosaurus is noted for having a body that would have been quite rigid and a skull that was fairly narrow, even when compared to other mosasaurs. The eyes of Plotosaurus also seem to have been fairly large in proportion to the head. Similar adaptations can be seen in the earlier opthalmosaurid ichthyosaurs that had gone extinct long before Plotosaurus appeared. As such Plotosaurus may have had a similar ecological niche as these ichthyosaurs, quickly diving down deep into the ocean depths, snatching up any deep sea fish and cephalopods (i.e. squids) before quickly returning to the surface to breathe in fresh air.
8 - Pannoniasaurus
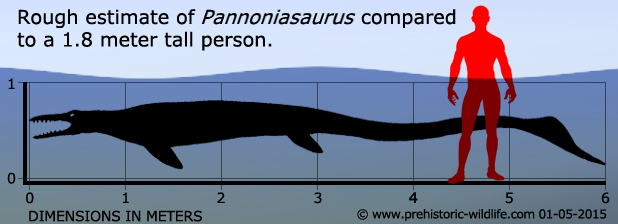
Described in 2012, Pannoniasaurus was described as the first mosasaur to be found in a fresh water deposit. This was big news as most fossils of mosasaurs have been found in what have been confirmed as marine (sea water) deposits, so confirmation that a mosasaur had been found in a fresh water deposit was proof mosasaurs would even enter rivers to hunt, kind of like how bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas) are known to do today. However the idea that mosasaurs hunted in fresh water was already being put forward before Pannoniasaurus was named, after all mosasaurs were air breathers and so did not need specialised gills suited to either salt water or fresh water to extract dissolved oxygen. An individual of another named genus called Goronyosaurus has been found in the country Niger, raising further speculation that this might have also been an example of a mosasaur that entered a river.
7 - Clidastes
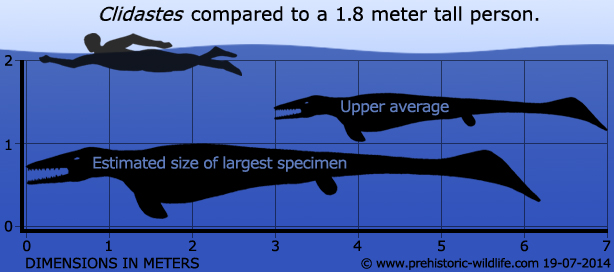
Most Clidastes were fairly small at no more than a few meters, though a few rare individuals seem to have grown a little larger. Clidastes makes the list as an individual of this genus has been found with a young juvenile preserved inside of it. Mosasaurs are known to have eaten each other but this juvenile specimen has no damage from stomach acid, and given its location within the adult, it seems that this little Clidastes was going to be born live. This indicates that mosasaurs were viviparous and did not lay eggs, something that had long been assumed about mosasaurs, given their body shapes would have made it next to impossible for them to move across dry land.
6 - Globidens

Globidens is another mosasaur that had developed a very special dietary preference. The name Globidens means ‘globe teeth’, a reference to the main teeth which were not pointed like other mosasaurs, but blunt and rounded. This was so the teeth would not splinter and break as Globidens closed its jaws against armoured prey such as ammonites. With the shell broken apart, the Globidens could then easily swallow the soft inner body of the ammonite.
5 - Proganthodon
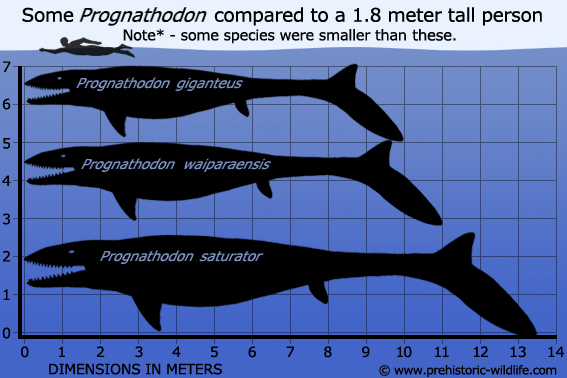
Like the aforementioned Globidens, Proganthodon also had blunt teeth for breaking up the hard shells of armoured prey, though not to the same extent as Globidens. Proganthodon however makes the list because in 2013 an individual Proganthodon was described which preserved soft tissue impression of the flesh of the tail. This revealed that Proganthodon had a bi-lobed tail, not a simple straight tail as had been assumed before. This was actually the second time that a mosasaur genus had shown the presence of a fluked tail, but it did prove that fluked tails were more common than previously thought, and perhaps a feature of all mosasaurs, triggering a shift towards all mosasaur genera being reconstructed as having tails.
4 - Dallasaurus
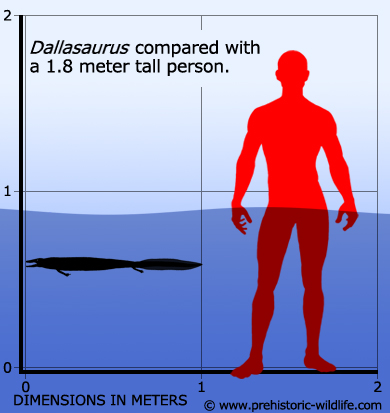
When described for the first time Dallasaurus was heralded as the most primitive mosasaur known. So primitive was Dallasaurus that it still had legs and feet, not flippers like later mosasaurs, and probably only entered the water to hunt and reach new areas. Study of Dallasaurus has helped to increase our understanding of how the first mosasaurs were directly related from terrestrial (land dwelling) ancestors, but very quickly adapted to life in the water to become apex predators by halfway through the Late Cretaceous.
3 - Mosasaurus

Ever since Jurassic World was released in 2015, Mosasaurus has become a fan favourite for anyone who is interested in ancient and massive marine predators. Mosasaurus was the first genus of mosasaur to be described by science, which in fact is why mosasaurs are called mosasaurs, they take their name from the first genus of their kind to be named. Mosasaurus has always been known to be big with most individuals around the 15 meter mark, though remains of one individual which are substantially larger suggest an upper size approaching 17.5 meters or more for rare individuals. Mosasaurus was also quite heavily built with powerful jaws, suggesting a preference for tougher but perhaps slower prey such as the giant sea turtles that lived during the same time as the mosasaurs.
2 - Tylosaurus

Tylosaurus was one of the larger mosasaurs, yet compared to some was more gracile (lightly built), meaning that while it may not have been as powerful, it was almost certainly faster and more agile, attributes that meant it was probably even more deadly than Mosasaurus given that even fewer animals could escape one. Tylosaurus was certainly a voracious predator and one that has shown us what kind of animals the big mosasaurs were eating through preserved stomach contents, with prey including fish, sharks, plesiosaurs, turtles, other mosasaurs and even sea birds. Tylosaurus is known by some of the most complete fossil remains, including even skin impressions.
1 - Platecarpus
Number one on the list is not the largest mosasaur, in fact it was only about a quarter of the length of the largest Mosasaurus. As a single genus however, Platecarpus has done more to advance our understanding of the mosasaurs than any other genus. Platecarpus was the first mossaur to reveal the presence of a bi-lobed fluked tail, long before the new specimen of the aforementioned Proganthodon. Platecarpus also has some of the most complete body impressions of scales, with detail of the snout, main body, and upper and lower portions of the tail known. Further to this one specimen of Platecarpus also has rock impressions of some of the internal organs preserved. It also shows the trachea and bronchi, revealing that not only did mosasaurs adapt their lungs in the same arrangement as the whales, but that mosasaurs had two working lungs. This has helped prove that the mosasaurs were closer to monitor lizards and not snakes as had previously been suggested by some. A Platecarpus specimen even has parts of the eye preserved which one day might help reveal such things as the colour of the eye as well as maybe how the eye worked. It is for all these reasons why the genus Platecarpus has made it to number 1.
If you will like even more information about mosasaurs then click right HERE for the main mosasaur article.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Random favourites
 |
 |
 |
 |





























